Here at theCUBE Research, we are dedicated to informing you about the latest developments shaping the future of AI. We’ll help you stay updated on emerging technologies, use cases, vendors, and real-world ROI.
In this research note, we partner with Jayeeta Putatunda, the director of the AI Center of Excellence at Fitch Group, to explore the strategic roadmap to next-generation AI in the financial services sector.
We’ll dive into what is happening in this fast-moving sector, which has historically been not only an early adopter of emerging technologies but a leader in driving meaningful innovation that ultimately spread across other industries.
Technically, we’ll explore how promising advancements in RAG frameworks, causal knowledge graphs, and AI reasoning will revolutionize decision-making within finance institutions. And what happens with AI in financial services will surely shape what happens elsewhere.
Watch the Podcast
Watch the latest episode of the Next Frontiers of AI podcast. We recently spoke with Jayeeta Putatunda, Director of the AI Center of Excellence at Fitch Group, about the evolution of AI in financial services. Their conversation highlighted the opportunities and challenges presented by GenAI, large language models (LLMs), retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) frameworks, and causal AI.
The State of AI in Financial Services
The financial services industry has long been at the forefront of technological innovation, and AI is no exception. Due to the sector’s highly regulated nature, financial institutions have been early adopters of AI-driven solutions to enhance risk management, automate processes, and optimize decision-making. Banks, investment firms, and insurance companies have leveraged predictive analytics, machine learning, and generative AI to improve fraud detection, credit risk assessment, and algorithmic trading.
In financial institutions, innovation cycles are moving at warp speed. In fact, we believe that we’ll see more innovation over the next couple of years than we just witnessed over the last two years with the advent of gen AI.
Generative AI and LLMs have created a crucial foundation for innovation, akin to the role of browsers 20 years ago. In the early days of the Internet, browsers served as a “gateway” to the online world. Now, Gen AI has opened a “gateway” into the domain of AI. However, just as the Internet age witnessed business value emerging from developments built on and around browsers, we will see the same phenomenon with generative AI in the business sector, especially in financial services.
In other words, the Gen AI arms race will not define the future of AI in financial services. The real competition will shift toward creating integrated AI model ecosystems that not only address the limitations of today’s AI but also open up countless new possibilities, including the promise of Agentic AI and AI-powered decision-making intelligence.
Financial institutions that recognize this change early — by focusing on building value on these Gen AI platforms — will lead the way in AI innovation and ROI.
A recent NVIDIA survey of over 600 financial institutions revealed that more than half of companies consider AI essential to establishing strategic competitiveness advantage. Furthermore, a whopping 98% of management expects to spend more on AI infrastructure in 2025.
This is true worldwide, as a survey conducted by EY revealed. In Europe, 90% of financial services executives have adopted AI to some degree, with 72% intending to increase their investments in the coming year.
Furthermore, according to adoption and spending tracking data provided by Enterprise Technology Research (ETR), the deployment of ML in financial institutions has reached 46%, representing by far the highest spending trajectory among all technology areas. According to ETR, a 58% Net Score indicates a highly elevated degree of planned spending to fuel new innovation cycles.
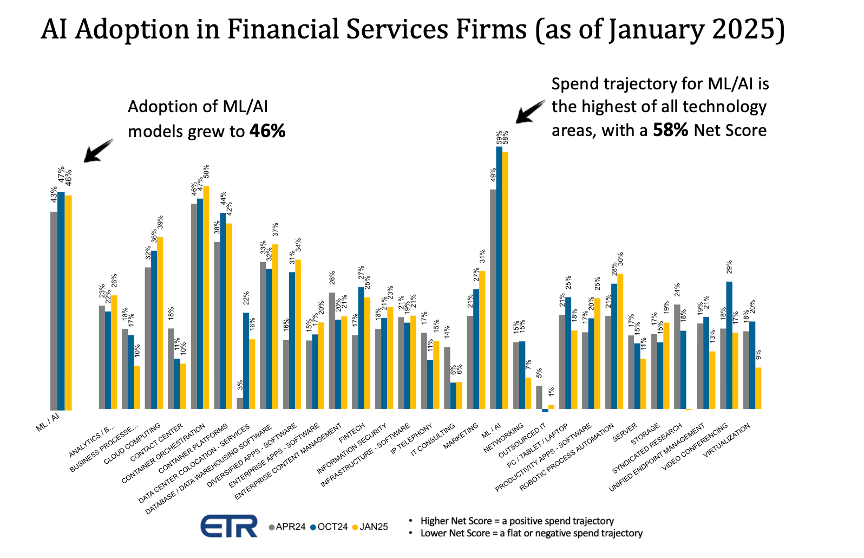
In addition, unlike most other industries, data analytics and predictive modeling use cases dominate in financial firms, which seek to harness vast amounts of their data to improve fraud detection, personalized services, market trend prediction, and investment risk management.
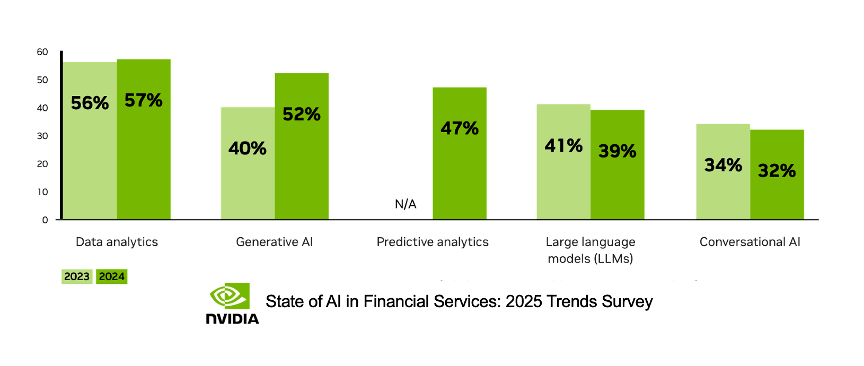
This highlights the key consideration when integrating analytics and decision-making in financial services firms. In this industry, firms must operate in an environment that requires real-time adaptability, high accuracy, and transparency. The critical need to integrate advanced AI models into essential applications distinguishes financial services in AI adoption while maintaining compliance and governance.
Pioneering the use of AI for structured financial modeling, risk assessment, and customer insights, the industry not only refines its own operations but also paves the way for AI adoption in other sectors. The methodologies and frameworks developed in finance—such as AI-powered regulatory compliance, auditability, and decision traceability—serve as benchmarks for industries like healthcare and supply chain manufacturing.
As Putatunda explained:
“Financial services has always led from the front in predictive analytics and deterministic models, but we must be cautious in our approach to GenAI. Given the industry’s regulatory nature and the high stakes involved, we are adopting AI carefully, ensuring governance and risk control at every stage.”
AI Limitations in Financial Use Cases
Over the past three years, predictive models and LLMs have become remarkably capable. They have spurred broader adoption of AI and laid a vital foundation for future AI applications. However, in most financial businesses, LLMs alone are insufficient to drive the high-value decision intelligence and analytics use cases they aim to envision.
This primarily stems from the limitations inherent in today’s LLMs. While they are highly impressive, these systems are constrained by their correlational designs. They navigate vast data lakes to identify associations, relationships, and anomalies, which are then used to predict or generate outcomes. Essentially, they operate based on brute force, processing enormous amounts of data through multiple layers of parameters and transformations to determine the next best token until they can predict a final outcome. However, this leads to a series of real-world limitations because they:
- Are prone to inaccuracies and bias
- Assume a prediction is a judgment
- Can confuse correlation with causation
- Lacks the concept of consequence
- Operate as “black boxes”
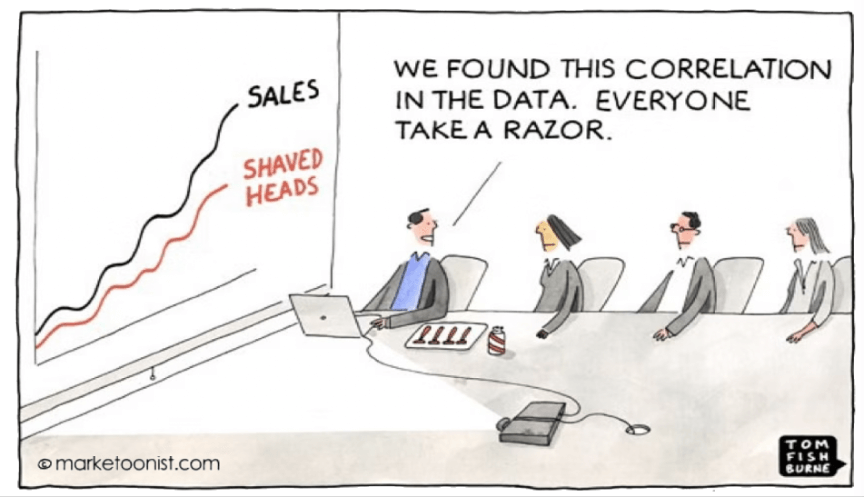
This challenge becomes even more evident when LLMs face more ambiguous, goal-oriented prompts, which are central to Agentic AI’s promise of value. For example, a recent study by Apple found that all state-of-the-art LLMs experienced significant declines in accuracy when faced with different versions of the same problem, altered values within a problem, or seemingly relevant yet ultimately irrelevant information.
In the financial services industry, Putatunda highlighted the three key challenges:
- Lack of Explainability –Financial professionals must understand how decisions are made and manage regulatory compliance and auditing.
- Non-Deterministic Behavior — LLMs can generate different outputs for the same input, posing risks when accuracy and consistency are paramount.
- Data Quality and Bias — Many models are trained on vast, unverified datasets, raising concerns about potential biases and the impact of synthetic data.
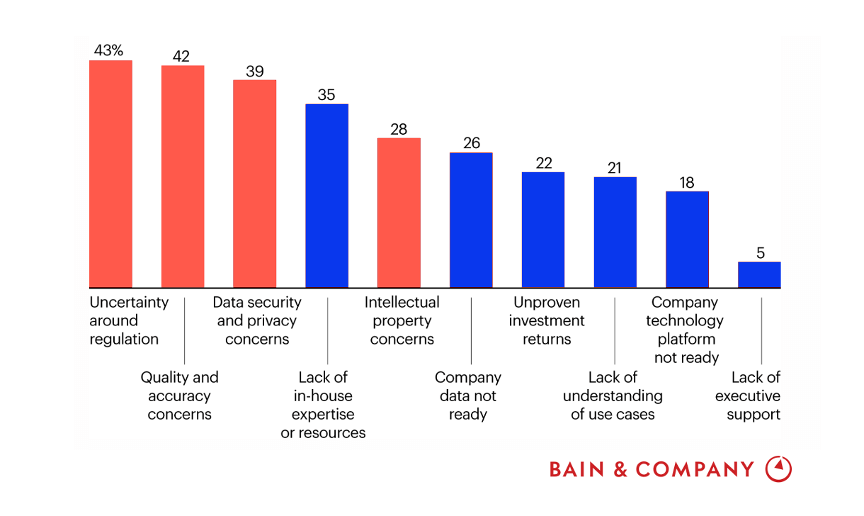
A recent study by Bain & Company on the state of AI in Financial Services made these concerns much clearer. As shown in the graph below, when asked what impeded the deployment of Generative AI and LLMs, worries about inaccuracies, regulatory reporting, and data privacy were predominant.
Next-Gen AI in Financial Services
These limitations highlight the necessity for more advanced AI techniques that improve explainability, reliability, and adaptability — along with the capability to support high-integrity decision-making in AI agents.
Putatunda has outlined five key considerations that create a framework for next-generation AI solutions in financial services:
- Ensure evidence-based grounding of AI models — GenAI and LLMs encounter challenges related to explainability and regulatory scrutiny. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) guarantees that every decision is supported by real-time, verifiable data that addresses these concerns.
- Establish a roadmap for transparent AI reasoning. LLMs and predictive models frequently encounter challenges related to hallucinations and outdated information. Advanced reasoning models can offer step-by-step reasoning and explainability, which enhances the audibility and trustworthiness of AI-driven financial decisions.
- Enhance risk management with causality — Traditional AI can highlight correlations, but causal AI uncovers the reasons behind market shifts. Techniques such as Structural Causal Models and Counterfactual Analysis enable firms to anticipate risks, refine stress-testing frameworks, and navigate economic uncertainty more effectively.
- Create decision agents by integrating RAG and Causal AI — AI in finance is advancing beyond basic predictions to enable judgment-driven decisions. The combination of RAG and causal inference creates autonomous, context-aware decision agents capable of analyzing dynamic financial environments and providing strategic recommendations.
- Envision new decision intelligence use cases — AI decision intelligence can reshape how financial services are offered, enhance market research, optimize investment strategies, and strengthen regulatory compliance. AI is no longer just an analytics tool; it’s a strategic partner in financial decision-making that will open countless new opportunities to create innovative, high-ROI use cases.
The Progression of RAG Frameworks
RAG frameworks are helping to address some of these challenges by combining LLM capabilities with structured information retrieval.
Putatunda outlined how RAG has evolved:
“We started with simple vector lookups, but the field has advanced significantly. We now have retrieval and reranking techniques that help differentiate between relevant and merely informative data, improving accuracy and relevancy.”
With the advent of AI agents in financial use cases, their ability to retrieve, understand, and apply knowledge from various sources will be crucial for financial decision-making. This progression naturally extends beyond traditional RAG techniques to more advanced RAG-based systems grounded in knowledge graphs (representing meaning, context, and relationships) and causal knowledge models (depicting dynamic cause-and-effect mechanisms). These constructs are critical to introducing a deeper layer of reasoning, interactivity, and situational awareness.
The pursuit of AI agents that can genuinely assist people in making decisions or even acting autonomously will make the concept of Causal RAGincreasingly beneficial. After all, making decisions is, by definition, a process of evaluating the dynamics of cause and effect.
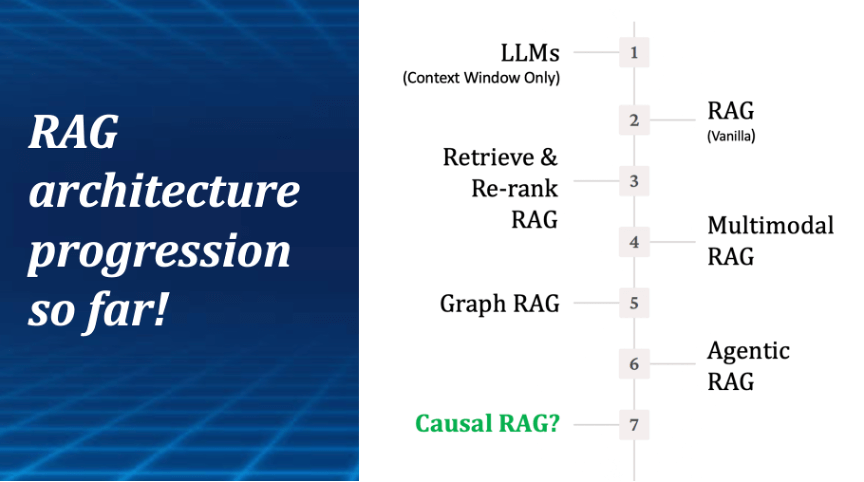
Causal RAG: AI Decision Intelligence
Knowledge graphs and Graph RAG create a critical foundation for enabling more capable AI decision intelligence by providing structured, contextualized knowledge that enhances AI’s reasoning ability.
Traditional AI models, particularly LLMs, rely heavily on statistical correlations, which limits their ability to understand domain-specific relationships and apply real-world logic and expertise. Knowledge graphsaddress this by organizing data into a network of entities and relationships, enabling AI to navigate complex interdependencies, understand semantics, and improve contextual meaning, which is critical for reasoning about a potential decision.
New advancements in Graph RAG enhance this capability by integrating retrieval mechanisms with knowledge graphs. This enables AI agents to access relevant, high-quality information dynamically rather than rely solely on static training data.
This approach allows AI systems to handle multi-step reasoning more effectively, improve contextual understanding, and support more precise decision-making across dynamic business environments, particularly finance. Financial institutions will gain deeper insights, greater accuracy, and actionable foresight by combining structured knowledge with RAG.
Putatunda noted.
“Knowledge graphs create a data lineage that allows LLMs to ground their outputs in factual, explainable relationships. This improves AI transparency and enhances compliance and governance frameworks.”
But, as Putatunda explained, decision-making is inherently a process of reasoning about cause-and-effect relationships and comparing the consequences of various decisions on a desired outcome. Simply put, the foundation of decision-making is causality, as it is what allows us to make judgments.
“This all became clearer when I stumbled upon a great paper called — Causal Parrots: LLMs Talk Causality But Are Not Causal — which I highly recommend reading.”

The Rise of Causal Knowledge Graphs
Importantly, knowledge graphs establish context and meaning among connected entities but do not inherently provide causality. This is where causal AI, an emerging branch of machine learning that understands cause-and-effect dynamics, comes into play.
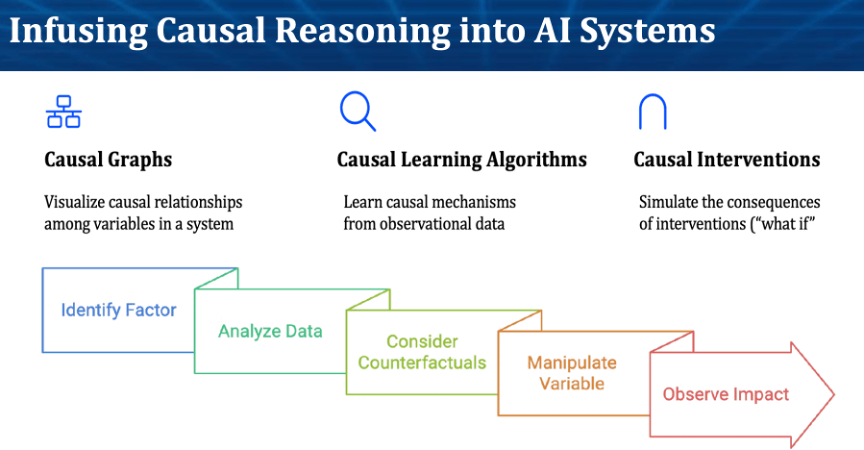
Building upon the success of knowledge graphs, new advancements in causal AI are now providing a framework — Causal Knowledge Graphs. With this new advancement, AI agents and systems will be better equipped to understand how outcomes change when the world around them changes, whether by intervention, creativity, or circumstance.
Since causal knowledge graphs are grounded in the mathematical principles of cause and effect, they enable AI algorithms to “reason” about why events occur and how various factors affect outcomes. Essentially, it’s AI that knows how and why things occur. The more AI understands this, the better it will be at helping humans make decisions and solve problems.
In simple terms, people naturally seek to understand “why” before taking action, which makes them causal by nature. It is also crucial for AI to be causal by nature. The potential impact of Causal AI on business could be substantial, as financial institutions depend on individuals (and systems) making real-time decisions. They will want to know what to do, how to do it, and why certain decisions are preferable to others.
In financial services, this advancement will lead to more accurate risk assessments, enhanced fraud detection, and improved customer insights. Root causes will be identified more easily, and various “what ifs” can be analytically evaluated to drive ongoing improvements.
Furthermore, for financial institutions that need to understand and audit AI outcomes, these models can also articulate the exact chain of events leading to an outcome in user-friendly language.
Putatunda sees four core game-changing new capabilities:
- Causal Discovery Algorithms analyze data to uncover hidden causal structures to understand real-world dependencies and how things actually work, not how we think they work. Today’s AI cannot identify and map real-world causal mechanisms.
- Causal Visualization illustrates relationships between variables, revealing connections, context, and meaning and the direction and strength of influence among them. Thus, people can understand how a system of variables interplays in an outcome and what truly influences an outcome.
- Confounders & Influences that identify confounding effects and rank which variables most impact an outcome, tracking how they change as conditions change. This allows financial firms to focus on the variables (and datasets) that are most critical to making a decision.
- Interventional Analysis simulates “what-if” scenarios, enabling financial professionals to test various decisions and understand their impact before taking action. With counterfactual reasoning, they can also model how emerging trends may influence an outcome.
Causal RAG further enhances AI decision intelligence by combining causal AI’s structured reasoning with RAG’s dynamic retrieval capabilities. Unlike traditional RAG, which retrieves and ranks information based on statistical similarity, Causal RAG prioritizes cause-and-effect relationships, enabling AI to generate insights grounded in real-world dependencies rather than mere correlations.
This approach allows financial institutions to simulate interventions, conduct counterfactual analyses, and improve explainability using real-time information. AI-driven decisions are more transparent, actionable, and aligned with complex real-world scenarios.
Putatunda noted.
“Statistical probabilities encode a static world, but causality tells us how that world changes when external conditions shift. AI needs to move from predictions to interventions — understanding what is likely to happen and why.
“In financial services, this is particularly crucial. We need AI models that help us answer ‘what-if’ questions, simulate alternative scenarios, and understand the factors influencing market behavior.”
The emerging capabilities of Causal Knowledge Graphs promise to make a tangible impact across various financial applications:
- Financial Optimization — Enables financial firms to play out countless scenarios to understand the consequences of various actions and analytically problem-solve.
- Risk Management — Structural causal models help banks assess macroeconomic factors affecting loan defaults, allowing for more robust risk assessments.
- Market Forecasting — By analyzing causal relationships between interest rates, inflation, and asset performance, financial institutions can make more informed investment decisions.
- Fraud Detection — Causal discovery algorithms identify hidden patterns and relationships in transaction data, improving fraud prevention strategies.
- Regulatory Compliance — Explainable AI models ensure compliance with stringent financial regulations by providing clear, auditable decision-making trails.
The next generation of AI in financial services will be defined by its ability to move beyond correlation-based predictions toward true decision intelligence. The integration of RAG, knowledge graphs, and causal AI is shaping a future where AI supports and enhances human decision-making.
As Putatunda concluded:
“The financial industry has always been at the cutting edge of AI adoption. By embracing causal AI, we can ensure that AI-driven decisions are not just accurate but also explainable, reliable, and actionable.”
With AI innovation accelerating at an unprecedented pace, financial institutions that invest in these advanced capabilities today will be best positioned to lead the future of AI-driven finance.
What to Do and When
This research, conducted with Jayeeta Putatunda, illustrates how new advancements in AI will reshape financial institutions’ decision-making and problem-solving while addressing a range of limitations in today’s predictive models. It will also play a significant role in shaping the future of businesses across all industries, as developments in AI within financial services will undoubtedly influence trends elsewhere.
- Perhaps the time is now to start preparing. We’d recommend you:
- Build competency in knowledge graphs and causal AI
- Evaluate the impact of causality on your use cases
- Engage with the array of vendors that provide causal AI solutions
- Experiment with the technology and build talent
We recommend checking out the Next Frontiers of AI Podcast on the SiliconANGLE Media YouTube Channel or on Spotify to hear from industry experts and pioneers.
Thanks for reading. Feedback is always appreciated.
As always, contact me if I can help you on this journey by messaging me here or on LinkedIn.