Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 Ransomware Report is out in advance of Black Hat this week, and the findings are both alarming and enlightening. This comprehensive analysis of the ransomware landscape from April 2023 to April 2024 reveals several key trends that organizations and security professionals need to be aware of. That’s why I was glad to have a chance to hop on today with Brett Stone-Gross, senior director of threat intelligence at Zscaler to walk through the report.
Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 Ransomware Report Overview with Brett Stone-Goss, watch the full episode of the SecurityANGLE here:
Record-Breaking Ransom Payment Signals Escalating Threats
Perhaps the most shocking revelation from the report is the unprecedented $75 million ransom payment made to the Dark Angels ransomware group. This figure nearly doubles the previous record for a publicly known ransomware payout, underscoring the increasingly high stakes of these attacks. I see this as a potential watershed moment that could very well embolden other ransomware groups to pursue similar high-value targets and demands.
Brett and I discussed the fact that the Dark Angels group’s success appears to stem from a highly targeted approach, focusing on a small number of large, lucrative targets rather than casting a wide net. This strategy not only yields higher payouts but also helps the group maintain a lower profile, potentially avoiding the scrutiny that comes with more prolific attack campaigns. It’s a concerning development that we believe other ransomware operators are likely to emulate in the coming year.
The report also shared the sobering reality that in 2023 alone, ransomware payments exceeded $1 billion, showing exactly why ransomware is so popular with threat actors — it’s an incredibly lucrative way to make a living.
Ransomware Attacks on the Rise Despite Law Enforcement Efforts
Despite numerous law enforcement operations, including the takedown of infrastructure and arrests of key players, ransomware attacks continue to surge. The Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 Ransomware Report revealed Zscaler’s cloud blocked 17.8% more ransomware attempts compared to the previous year, while attacks identified through data leak site analysis skyrocketed by 57.8%. This resilience, especially in the face of increased law enforcement pressure, speaks to the adaptability and persistence of ransomware groups.
The report highlights several major law enforcement actions, including “Operation Duck Hunt” against the Qakbot botnet and “Operation Endgame,” which targeted multiple initial access brokers simultaneously. While these operations disrupted some ransomware ecosystems, many groups quickly regrouped and evolved their tactics. This cat-and-mouse game between cybercriminals and law enforcement is likely to intensify in the coming years.
Industry and Geographic Trends
Based on data from data leak sites, the Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 Ransomware Report identified manufacturing as the most targeted sector, accounting for more than double the attacks of any other industry, with healthcare and technology rounding out the top three most impacted verticals — which tracks with our research. While not as popular as the top three most impacted verticals, education, financial services, retail & wholesale, and the legal industry are proving attractive to threat actors as well.
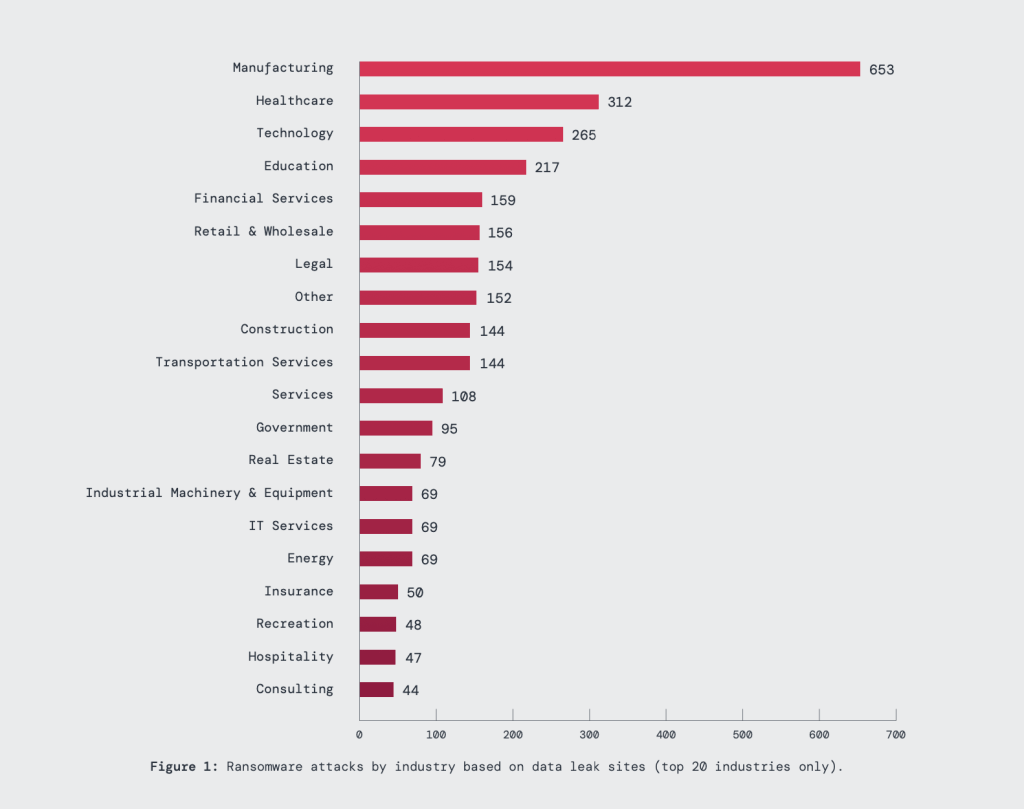
This targeting of critical infrastructure and data-rich industries is likely to continue as these sectors often have a higher propensity to pay ransoms due to operational criticality or sensitive data concerns.
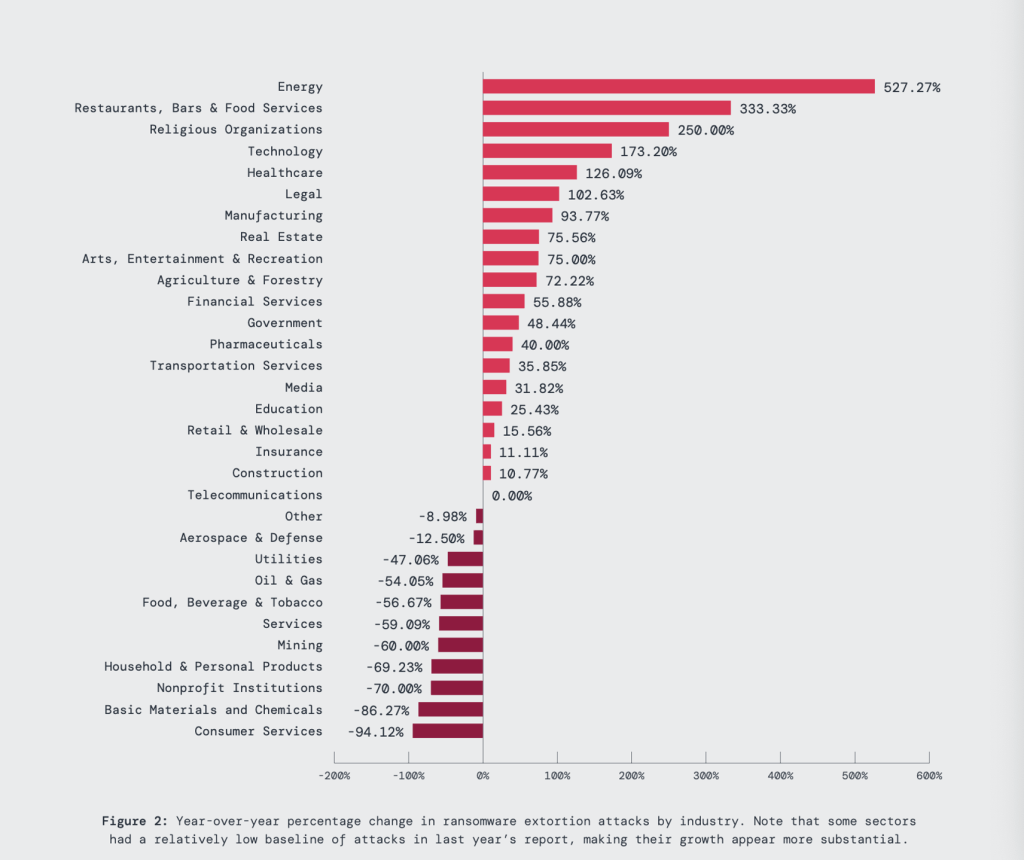
The report also examined year-over-year trends across industries, with the energy sector experiencing a 527.27% increase in ransomware attacks, followed by restaurants, bars & food services at 333.33 and religious organizations experiencing a 250% increase. A reality of today’s world is that the more we digitize, the more we collectively open ourselves up to ransomware attacks. Think about this solely as it relates to the rise of attacks on restaurants, bars & food services. Online ordering systems, the use of QR codes for menus, and advanced point-of-sale systems all present attractive opportunities for threat actors to swoop in and take advantage.
Geographically, the United States remains the primary target, experiencing nearly 50% of all ransomware attacks globally. The UK, Germany, Canada, and France follow as the next most targeted countries. This concentration of attacks in developed economies with high-value targets is not surprising, but it does highlight the need for improved international cooperation in combating these threats.
Evolving Tactics and New Ransomware Families
The Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 Ransomware Report identified 19 new ransomware families during the analysis period, bringing the total tracked to 391. This proliferation of ransomware variants speaks to the ongoing innovation in the cybercriminal ecosystem. The most active families were LockBit (22.1%), BlackCat (9.2%), and 8Base (7.9%), demonstrating the dominance of certain groups in the ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) market.
One particularly concerning trend Brett and I discussed is the increasing use of voice-based social engineering attacks to gain initial access to corporate networks. Groups like Scattered Spider and the Qakbot threat actors have employed sophisticated vishing techniques to deceive employees and bypass traditional security measures. This human-centric approach to breaching defenses is likely to become more prevalent as technical security measures improve.
The Impact of AI and the Need for Zero Trust
Looking ahead to 2025, the report predicts that ransomware attackers will increasingly leverage generative AI to create more effective, personalized, and localized campaigns. This could lead to more convincing phishing emails, voice cloning for social engineering attacks, and potentially even AI-driven malware that can adapt to evade detection.
In response to these evolving threats, it’s abundantly clear that a unified approach to timely patching and vulnerability management, alongside a zero trust architecture that can provide protection when patches are not yet available is business mission critical.
By minimizing the attack surface, preventing initial compromise, eliminating lateral movement, and stopping data loss, a zero trust architecture can significantly reduce the risk and impact of ransomware incidents.
CISA’s Comprehensive List of Vulnerabilities is a Valuable Resource
The report mentions CISA’s comprehensive list of known vulnerabilities, including those actively being exploited. With the rapid rise in internet-connected assets and devices VPNs, routers, gateways, and other remotely connected tech are incredibly easy for threat actors to find and exploit.
Zero trust architecture, SSE, and SASE, all of which are based on granular access control policies, can go a long way toward helping organizations combat this exploitation of vulnerabilities. Regularly viewing CISA’s Known Vulnerabilities Catalog and monitoring and prioritization the mitigation of vulnerabilities mentioned is an important task for cybersecurity pros, as are requiring strong passwords and multifactor authentication (MFA), requiring password changes on a regular cadence regardless of how unpopular that might be with employees, and monitoring continuously for suspicious activity.
Here’s a look at some of the most prevalent vulnerabilities identified by ThreatLabz from April 2023 to April 2024: ConnectWise’s ScreenConnect, Cisco’s ASA and FTD software, Cisco’s remote access VPN feature, and the Citrix NetScaler ACD and NetScaler Gateway. These are by no means all vulnerabilities identified and tracked by CISA, but the ones that should command your immediate attention.

Regulatory Landscape and Disclosure Trends
The report also touches on the impact of new SEC cybersecurity disclosure rules, which came into effect in December 2023. These regulations mandate timely reporting of material cybersecurity incidents and require detailed information about a company’s cybersecurity risk management and governance. While this increased transparency is likely to shed more light on the true scale and impact of ransomware attacks, potentially leading to improved defensive strategies and increased pressure on organizations to bolster their security postures, it’s a reality that some companies are failing to comply with these new cybersecurity rules. While the SEC’s new disclosure rules mandate the submission of detailed assessments and quantitative data about the financial and operational implications of cyber incidents, in a number of instances, even some well-known companies are failing to comply.
Conclusion
The Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 Ransomware Report is a finger on the pulse of the current state of the ransomware threat landscape, and the findings showcased here are extremely valuable. Ransomware continues to be an outsized threat for organizations of all sizes across all geos, and there is every reason to believe that threat will continue — and continue to grow apace. The record-breaking ransom payment and what’s likely ahead on that front, a continued rise in attack volume, and the continuous evolution of tactics all point to a threat that is far from contained. Organizations must prioritize robust, layered defenses with a focus on zero trust principles, continuous monitoring, and rapid incident response capabilities.
The report’s predictions for 2025, including the adoption of AI by attackers and the shift toward more targeted, high-value attacks, suggest that the ransomware threat will continue to evolve and present new challenges. As such, staying informed about the latest trends and adopting proactive security measures will be more critical than ever for organizations looking to protect themselves from the ever-present specter of ransomware — that’s why research like this is so valuable.
Grab the Zscaler ThreatLabz Ransomware Report here and if you’re at Black Hat this week, don’t hesitate to reach out to Brett Stone-Gross if you’d like to discuss.
Body image credits: Zscaler ThreatLabz, header image credit: Pexels, Mati Mango
Other relevant coverage:
Zscaler’s Executive Insights Mobile App: Serving Up Better Experiences
Unpacking Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 AI Security Report
CISA’s Secure by Design Pledge Continues to Build Momentum: Is it Basic? Maybe, but it’s a Start



